Condition
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Infectious
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Genomics
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Pulmonary / Infectious
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Others
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Others
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Others
- Genetics
- Others
- Gastrointestinal / Skeletomuscular
- Gastrointestinal / Skeletomuscular
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Lifestyle Packages
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Allergy
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Others
- Blood Disorders
- Top tests
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Fever
- Fever
- Blood Disorders
- Blood Disorders
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Profile
- Kidney Disease
- Kidney Disease
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Thyroid Disorder
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Allergy
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Liver Disease
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Liver Disease
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Anemia
- Anemia
- Anemia
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Anemia
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Thyroid Disorder
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Fever
- Allergy
- Liver Disease
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Arthritis
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Kidney Disease
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Allergy
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Kidney Disease
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Allergy
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Allergy
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Infertility
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Allergy
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Infertility
- Top tests
- Thyroid Disorder
- Top tests
- Allergy
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Infertility
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Liver Disease
- Kidney Disease
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Infertility
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Arthritis
- Arthritis
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Infertility
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- PCOD
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Fever
- PCOD
- Kidney Disease
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Liver Disease
- Thyroid Disorder
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- PCOD
- Top tests
- Arthritis
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Kidney Disease
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Allergy
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Thyroid Disorder
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Kidney Disease
- Liver Disease
- Infertility
- Top tests
- Anemia
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Bone Health
- Cancer
- Fatty Liver

Tests
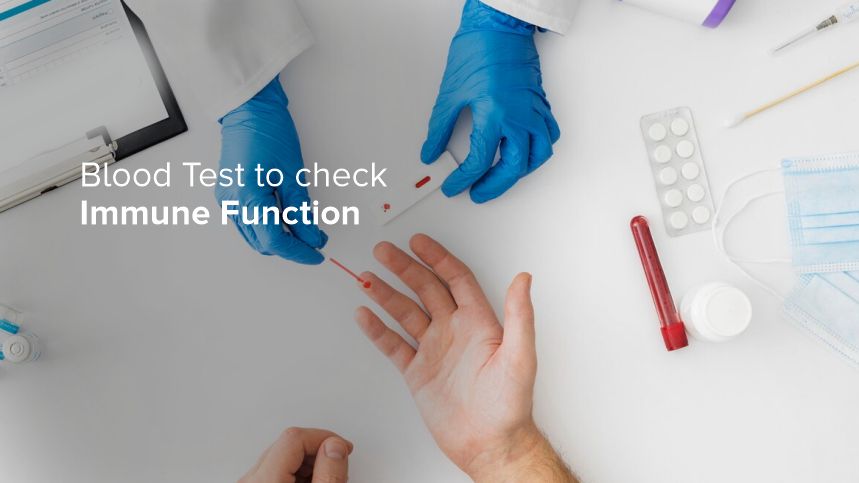
Maintaining good health is a top priority for many individuals, and understanding how your immune system functions plays a vital role in this. A robust immune system is your body’s defense against infections and diseases. One of the most effective ways to assess the state of your immune system is through a blood test. In this blog, we’ll delve into the intricacies of blood tests for immune function, why they are important, and what you can expect from the results.
What is Immune Function?
Before diving into blood tests, it's essential to understand what immune function entails. Your immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to protect your body from harmful substances, germs, and cell changes that could make you ill. The primary components of the immune system include white blood cells, antibodies, the complement system, the lymphatic system, the spleen, the thymus, and the bone marrow.
Why Check Immune Function?
Checking immune function is crucial for several reasons:
- Early Detection of Diseases: Assessing immune function can help detect diseases at an early stage when they are more treatable.
- Monitoring Existing Conditions: For those with chronic illnesses or autoimmune conditions, regular monitoring can help manage the disease effectively.
- Before Medical Treatments: Prior to certain medical treatments, especially those that suppress the immune system like chemotherapy, it is vital to understand the current state of your immune function.
- General Health Assessment: Regular check-ups can provide a comprehensive overview of your overall health and identify any potential issues before they become serious.
Types of Blood Tests for Immune Function
There are several types of blood tests that can be performed to evaluate different aspects of the immune system. Here are some of the most common ones:
1. Complete Blood Count (CBC)
A CBC is the most routine blood test used to assess overall health and detect a variety of disorders, such as anemia, infection, and many other diseases. It measures:
- Red blood cell count
- White blood cell count
- Hemoglobin levels
- Hematocrit levels
- Platelet count
2. Immunoglobulin Levels
This test measures the levels of immunoglobulins (antibodies) in the blood, which are critical for the immune response. The primary types of immunoglobulins include IgA, IgG, and IgM. Abnormal levels can indicate immune deficiencies or autoimmune diseases.
3. Lymphocyte Subset Panel
Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell vital for the immune response. This test analyzes the different types of lymphocytes (T cells, B cells, and Natural Killer cells) to provide detailed information about the immune system’s functionality.
4. C-Reactive Protein (CRP) Test
CRP is a substance produced by the liver in response to inflammation. This test measures the level of CRP in the blood, which can indicate acute inflammation and help diagnose conditions like infections and chronic inflammatory diseases.
5. Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)
The ESR test measures how quickly red blood cells settle at the bottom of a test tube. A faster-than-normal rate may indicate inflammation in the body, which can be a sign of immune system problems.
Preparing for a Blood Test
Preparing for a blood test to check immune function typically involves the following steps:
- Fasting: Some tests may require you to fast for several hours before the test.
- Medication: Inform your healthcare provider about any medications you are taking, as some can affect the results.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water before the test to make the blood draw easier.
Interpreting the Results
Interpreting blood test results can be complex and should always be done by a healthcare professional. Here is a general guide to what some of the results might indicate:
- High White Blood Cell Count: May indicate an infection, inflammation, or an immune system disorder.
- Low White Blood Cell Count: Could suggest a risk for infections or potential bone marrow problems.
- Abnormal Immunoglobulin Levels: May point to immune deficiencies or autoimmune diseases.
- High CRP Levels: Indicate acute inflammation which could be due to infection or chronic inflammatory diseases.
If you experience symptoms such as frequent infections, prolonged fatigue, unexplained inflammation, or other health issues, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional who may recommend a blood test to check your immune function.
Conclusion
Understanding your immune function through blood tests can provide valuable insights into your overall health and help detect potential health issues early on. Whether for routine health checks, managing chronic conditions, or preparing for specific medical treatments, these tests are essential tools for maintaining optimal health.
Taking a proactive approach to your health by regularly monitoring your immune function can lead to better outcomes and improved well-being. If you have any questions or concerns about your immune system, don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider for personalized advice and testing.
WANT TO BOOK HEALTH CHECKUP ?
Categories
Top tests
114
Lifestyle Packages
47
Diabetes
58
Preventive Health Checkup
60
Infectious
1
Heart Disease & Hypertension
38
Genomics
1
Others
81
Pulmonary / Infectious
1
Genetics
1
Gastrointestinal / Skeletomuscular
2
Blood Banking & Transfusion
16
Vitamin Deficiency
12
Allergy
9
Blood Disorders
3
Fever
4
Profile
1
Kidney Disease
8
Thyroid Disorder
5
Liver Disease
6
Anemia
5
Arthritis
4
Infertility
6
PCOD
3
Bone Health
1
Cancer
1
Fatty Liver
1