Condition
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Infectious
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Genomics
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Pulmonary / Infectious
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Others
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Others
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Others
- Genetics
- Others
- Gastrointestinal / Skeletomuscular
- Gastrointestinal / Skeletomuscular
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Lifestyle Packages
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Allergy
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Others
- Blood Disorders
- Top tests
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Fever
- Fever
- Blood Disorders
- Blood Disorders
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Profile
- Kidney Disease
- Kidney Disease
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Thyroid Disorder
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Allergy
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Liver Disease
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Liver Disease
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Anemia
- Anemia
- Anemia
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Anemia
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Thyroid Disorder
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Fever
- Allergy
- Liver Disease
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Arthritis
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Kidney Disease
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Allergy
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Kidney Disease
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Allergy
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Allergy
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Infertility
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Allergy
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Infertility
- Top tests
- Thyroid Disorder
- Top tests
- Allergy
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Infertility
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Liver Disease
- Kidney Disease
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Infertility
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Arthritis
- Arthritis
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Infertility
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- PCOD
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Fever
- PCOD
- Kidney Disease
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Liver Disease
- Thyroid Disorder
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- PCOD
- Top tests
- Arthritis
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Kidney Disease
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Allergy
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Thyroid Disorder
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Kidney Disease
- Liver Disease
- Infertility
- Top tests
- Anemia
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Bone Health
- Cancer
- Fatty Liver

Tests
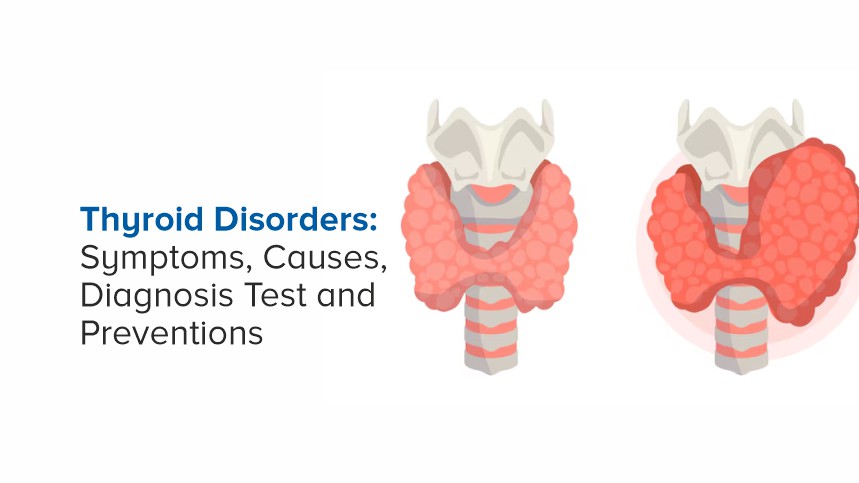
The thyroid gland, a small butterfly-shaped organ located at the front of your neck, plays a vital role in regulating many of your body’s functions. From maintaining metabolism to influencing energy levels, this powerful gland governs several aspects of overall health. However, when something goes wrong with the thyroid, it can lead to a wide array of health challenges.
This guide will comprehensively cover thyroid disorders, focusing on their symptoms, causes, diagnostic tests, and prevention strategies. Whether you’re dealing with an ongoing thyroid issue or seeking to improve your understanding of these conditions, this article will equip you with the knowledge to make well-informed health decisions.
Types of Thyroid Disorders
Thyroid disorders primarily fall into two broad categories based on their impact on hormone production:
- Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid): Occurs when the thyroid gland produces insufficient thyroid hormones. It can slow down metabolic processes, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and depression.
- Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid): Involves excessive thyroid hormone production, speeding up metabolism. Symptoms may include rapid weight loss, nervousness, and irregular heartbeat.
Other common thyroid disorders include:
- Goiter: Abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland.
- Thyroid Nodules: Lumps or masses within the thyroid, which could result from either benign or malignant processes.
- Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: An autoimmune condition leading to hypothyroidism.
- Graves’ Disease: Another autoimmune disorder that commonly causes hyperthyroidism.
- Thyroid Cancer: A rare but serious condition involving malignant tissue growth in the thyroid gland.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Thyroid Disorders
Many thyroid disorders have symptoms that overlap with other health issues, making early diagnosis challenging. Below are the most common manifestations to watch out for:
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
- Fatigue and sluggishness
- Unexplained weight gain
- Cold intolerance
- Constipation
- Dry skin and thinning hair
- Depression or memory issues
- Puffy face or hoarseness
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
- Increased appetite coupled with unintentional weight loss
- Heat intolerance and excessive sweating
- Irritability or anxiety
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Tremors in hands or fingers
- Frequent bowel movements
- Bulging eyes (in cases of Graves’ disease)
If you experience any of these symptoms for an extended period, consult your healthcare provider to explore potential thyroid issues.
What Causes Thyroid Disorders?
A range of factors can influence the proper functioning of the thyroid gland. Below are several potential causes:
Genetic Factors:
Thyroid problems often run in families. If your close relatives have a history of thyroid disease, you might be more likely to develop one as well.
Autoimmune Disorders:
Conditions such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or Graves’ disease occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, affecting its function.
Dietary Deficiencies or Excesses:
A lack of iodine in the diet is a common cause of hypothyroidism. Excessive iodine consumption can also trigger thyroid dysfunction.
Medications and Treatments:
Certain medications, like lithium or interferon-alpha, can disrupt thyroid hormone production. Radiation therapy to the neck area can also impact thyroid function.
Underlying Health Conditions:
Viral or bacterial infections, pituitary gland disorders, or severe stress may lead to temporary or chronic thyroid problems.
How Are Thyroid Disorders Diagnosed?
Diagnosing thyroid issues typically involves a mix of clinical evaluation and laboratory tests. Here’s what to expect when visiting a doctor:
Physical Exam:
Your physician may start with a thorough physical examination to look for signs of an overactive or underactive thyroid, such as swelling in the neck.
Blood Tests:
These are the gold standard for diagnosing thyroid function. Key tests include:
- TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone) – to assess whether hormone production is balanced.
- T3 (Triiodothyronine), T4 (Thyroxine) – to measure the levels of vital thyroid hormones in your blood.
Imaging Tests:
Ultrasound or a radioactive iodine uptake scan may be recommended to evaluate the thyroid’s physical structure and detect abnormalities such as nodules.
Biopsy:
If thyroid nodules are present and appear suspicious, a fine-needle aspiration biopsy may be performed to rule out thyroid cancer.
Preventing Thyroid Disorders
While it’s impossible to prevent genetic or autoimmune causes, adopting a proactive lifestyle can help reduce the risk of developing thyroid disorders or assist in their management.
Maintain Adequate Iodine Intake: Ensure your diet includes the recommended daily allowance (RDA) of iodine. Foods like iodized salt, dairy products, eggs, and seaweed can help meet your body’s iodine needs. However, excessive iodine intake should be avoided.
Adopt a Consistent, Healthy Diet: Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Selenium-rich foods like nuts, eggs, and fish may also support thyroid health.
Manage Stress Levels:Since stress can exacerbate certain thyroid conditions, incorporating relaxation techniques like yoga and meditation can help maintain hormonal balance.
Regular Check-ups: Routine health check-ups, especially when a family history of thyroid issues exists, can catch potential problems before they worsen.
How Ampath Labs Can Help
Early and accurate diagnosis is the key to managing thyroid disorders effectively. At Ampath Labs, we offer comprehensive diagnostic tests for thyroid health, including TSH, T3, T4, and antibody tests. Our cutting-edge technology and team of certified professionals ensure precision and reliability in every report. With a convenient network of collection centers, Ampath Labs is your trusted partner in proactive healthcare. Contact us today to schedule your thyroid health check!
WANT TO BOOK HEALTH CHECKUP ?
Categories
Top tests
114
Lifestyle Packages
47
Diabetes
58
Preventive Health Checkup
60
Infectious
1
Heart Disease & Hypertension
38
Genomics
1
Others
81
Pulmonary / Infectious
1
Genetics
1
Gastrointestinal / Skeletomuscular
2
Blood Banking & Transfusion
16
Vitamin Deficiency
12
Allergy
9
Blood Disorders
3
Fever
4
Profile
1
Kidney Disease
8
Thyroid Disorder
5
Liver Disease
6
Anemia
5
Arthritis
4
Infertility
6
PCOD
3
Bone Health
1
Cancer
1
Fatty Liver
1