Condition
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Infectious
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Genomics
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Pulmonary / Infectious
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Others
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Others
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Others
- Genetics
- Others
- Gastrointestinal / Skeletomuscular
- Gastrointestinal / Skeletomuscular
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Lifestyle Packages
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Allergy
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Others
- Blood Disorders
- Top tests
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Fever
- Fever
- Blood Disorders
- Blood Disorders
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Profile
- Kidney Disease
- Kidney Disease
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Thyroid Disorder
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Allergy
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Liver Disease
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Liver Disease
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Anemia
- Anemia
- Anemia
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Anemia
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Thyroid Disorder
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Fever
- Allergy
- Liver Disease
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Arthritis
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Kidney Disease
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Allergy
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Kidney Disease
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Allergy
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Allergy
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Infertility
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Allergy
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Infertility
- Top tests
- Thyroid Disorder
- Top tests
- Allergy
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Infertility
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Liver Disease
- Kidney Disease
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Infertility
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Arthritis
- Arthritis
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Infertility
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- PCOD
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Fever
- PCOD
- Kidney Disease
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Liver Disease
- Thyroid Disorder
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- PCOD
- Top tests
- Arthritis
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Kidney Disease
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Allergy
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Thyroid Disorder
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Kidney Disease
- Liver Disease
- Infertility
- Top tests
- Anemia
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Bone Health
- Cancer
- Fatty Liver

Tests
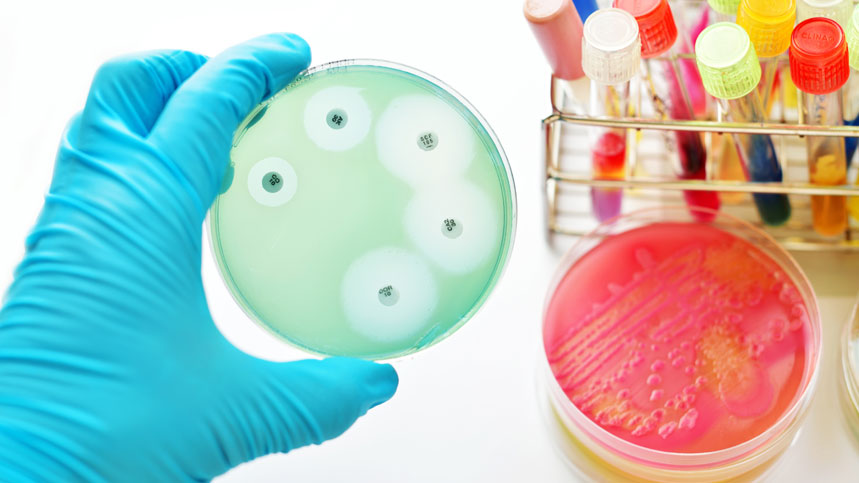
Antibiotic sensitivity testing is a critical tool used in microbiology. It allows scientists to determine the effectiveness of antibiotics on bacterial pathogens. This test is essential in the management of bacterial infections and provides healthcare professionals with critical information. The results of an antibiotic sensitivity test guide clinicians in choosing the right antibiotic therapy for the patient.
Bacterial infections are becoming increasingly difficult to manage due to the emergence of antibiotic resistance. An antibiotic sensitivity test provides an understanding of the epidemiology of resistant bacteria and their patterns of antibiotic sensitivity. This information is essential for clinical decision-making and for the development of new antibiotics. The test helps healthcare professionals understand the most effective treatment options for their patients.
How is Antibiotic sensitivity testing performed?
Antibiotic sensitivity testing is typically performed using a variety of techniques. The most commonly used method is the Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion method. This method uses a standardized amount of antibiotic on a disk, which is then placed onto a culture plate. The plate is incubated, and the zone of inhibition, or the area around the disk where bacterial growth is inhibited, is measured. This measurement is used to determine the effectiveness of the antibiotic against the bacterial pathogen.
The results of the antibiotic sensitivity test are interpreted using standardized guidelines. The susceptibility or resistance of a bacterial isolate is determined by comparing the zone of inhibition measurement to a standard table. This table contains interpretive breakpoints that define the susceptibility, intermediate, or resistance of each antimicrobial agent.
Antibiotic sensitivity testing is particularly important in situations where antibiotic resistance is suspected. In these cases, the test helps identify which antibiotics are most effective against the bacteria. This information can guide healthcare professionals in selecting the best antibiotic therapy for their patients. It can also help prevent the overuse of broad-spectrum antibiotics, which contributes to the development of antibiotic resistance.
Conclusion
Antibiotic sensitivity testing is a critical tool in microbiology. It provides healthcare professionals with information on the most effective antibiotic therapy for bacterial infections. This test is particularly important in situations where antibiotic resistance is suspected. The results of the test can guide clinicians in selecting targeted antibiotic therapy and in preventing the overuse of broad-spectrum antibiotics. As antibiotic resistance continues to be a significant public health concern, the importance of antibiotic sensitivity testing in managing bacterial infections cannot be overstated.
WANT TO BOOK HEALTH CHECKUP ?
Categories
Top tests
114
Lifestyle Packages
47
Diabetes
58
Preventive Health Checkup
60
Infectious
1
Heart Disease & Hypertension
38
Genomics
1
Others
81
Pulmonary / Infectious
1
Genetics
1
Gastrointestinal / Skeletomuscular
2
Blood Banking & Transfusion
16
Vitamin Deficiency
12
Allergy
9
Blood Disorders
3
Fever
4
Profile
1
Kidney Disease
8
Thyroid Disorder
5
Liver Disease
6
Anemia
5
Arthritis
4
Infertility
6
PCOD
3
Bone Health
1
Cancer
1
Fatty Liver
1