Condition
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Infectious
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Genomics
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Pulmonary / Infectious
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Others
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Others
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Others
- Genetics
- Others
- Gastrointestinal / Skeletomuscular
- Gastrointestinal / Skeletomuscular
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Lifestyle Packages
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Allergy
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Others
- Blood Disorders
- Top tests
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Fever
- Fever
- Blood Disorders
- Blood Disorders
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Profile
- Kidney Disease
- Kidney Disease
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Thyroid Disorder
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Allergy
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Liver Disease
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Liver Disease
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Anemia
- Anemia
- Anemia
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Anemia
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Thyroid Disorder
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Fever
- Allergy
- Liver Disease
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Arthritis
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Kidney Disease
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Allergy
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Kidney Disease
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Allergy
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Allergy
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Infertility
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Allergy
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Infertility
- Top tests
- Thyroid Disorder
- Top tests
- Allergy
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Infertility
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Liver Disease
- Kidney Disease
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Infertility
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Arthritis
- Arthritis
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Infertility
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- PCOD
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Fever
- PCOD
- Kidney Disease
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Liver Disease
- Thyroid Disorder
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- PCOD
- Top tests
- Arthritis
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Kidney Disease
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Allergy
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Thyroid Disorder
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Kidney Disease
- Liver Disease
- Infertility
- Top tests
- Anemia
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Bone Health
- Cancer
- Fatty Liver

Tests
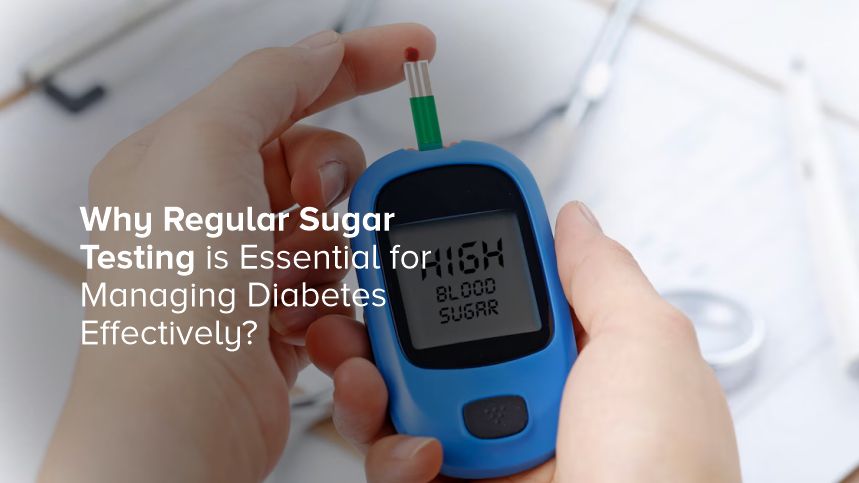
In a world where chronic illnesses are on the rise, diabetes stands out as one of the most prevalent and challenging conditions to manage. With millions of people affected globally, it's essential to understand how regular sugar testing plays a critical role in effective diabetes management. Here will guide you through the importance of consistent monitoring, offer practical tips, and share insights that can help you lead a healthier life.
Understanding Diabetes and Its Impact
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how your body processes blood sugar. There are two main types—Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 diabetes occurs when the body doesn't produce insulin, while Type 2 is characterized by insulin resistance. Both types require careful management to prevent complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, and vision problems.
Managing diabetes involves a multi-faceted approach, including diet, exercise, medication, and regular sugar testing. The latter is especially crucial as it provides real-time data about your blood sugar levels, helping you make informed decisions about your health.
The Science Behind Blood Sugar Levels
Blood sugar, or glucose, is the primary source of energy for our bodies. It comes from the food we eat, particularly carbohydrates. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, helps regulate blood sugar levels by allowing glucose to enter cells for energy. In individuals with diabetes, this process is disrupted, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
High blood sugar levels can cause a range of symptoms, from fatigue and frequent urination to more severe complications if left unchecked. Regular sugar testing allows you to monitor these levels and take corrective actions promptly.
Why Regular Sugar Testing Matters
Consistent monitoring of blood sugar levels is vital for several reasons. First, it helps you understand how different foods, activities, and medications affect your blood sugar. This knowledge empowers you to make better lifestyle choices and manage your condition more effectively.
Second, regular testing can alert you to dangerously high or low blood sugar levels, enabling you to take immediate action. This is particularly important for those on insulin therapy, as incorrect dosages can lead to severe hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
Tools for Monitoring Blood Sugar
Modern technology offers various tools to help you monitor your blood sugar levels. Glucometers are the most common devices, allowing you to check your levels at home with a small drop of blood. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) are another option, providing real-time data through a sensor worn on the body.
These tools not only make monitoring easier but also offer features like data logging and trend analysis. This information can be shared with your healthcare provider to tailor your treatment plan more effectively.
How Often Should You Test Your Blood Sugar?
The frequency of blood sugar testing varies depending on the type of diabetes and individual treatment plans. For Type 1 diabetes, it's generally recommended to test multiple times a day, including before meals, after meals, and at bedtime. For Type 2 diabetes, the frequency may be lower but should still be consistent.
Your healthcare provider will guide you on the optimal testing schedule based on your specific needs. It's crucial to follow their advice to maintain stable blood sugar levels and prevent complications.
The Role of Diet in Blood Sugar Management
Diet plays a significant role in managing diabetes. Carbohydrates have the most immediate impact on blood sugar levels, so it's essential to monitor your intake. Focus on complex carbohydrates like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, which have a slower impact on blood sugar.
Protein and healthy fats also play a role in stabilizing blood sugar levels. Incorporate lean meats, fish, nuts, and seeds into your diet to maintain balanced nutrition. Regular sugar testing will help you understand how different foods affect your blood sugar and allow you to make necessary adjustments.
Exercise and Blood Sugar Levels
Physical activity is another crucial component of diabetes management. Exercise helps lower blood sugar levels by increasing insulin sensitivity and allowing cells to use glucose more efficiently. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
Regular sugar testing before and after exercise will help you understand how physical activity affects your blood sugar levels. This information is vital for planning your workouts and preventing exercise-induced hypoglycemia.
The Impact of Medication on Blood Sugar
Medications play a vital role in managing diabetes, especially for those who require insulin or other glucose-lowering drugs. Regular sugar testing is essential to ensure that your medication is working effectively and to make necessary adjustments.
Your healthcare provider may recommend insulin therapy, oral medications, or a combination of both. It's crucial to follow their guidelines and monitor your blood sugar levels to avoid complications.
Recognizing and Managing Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, can occur due to various factors, including excessive insulin, prolonged fasting, or intense exercise. Symptoms include shakiness, confusion, and dizziness. Regular sugar testing helps you recognize the early signs of hypoglycemia and take corrective action.
If you experience low blood sugar, consume a fast-acting carbohydrate like glucose tablets, juice, or candy. Recheck your levels after 15 minutes and repeat if necessary. Always carry a source of fast-acting carbohydrates with you to manage unexpected episodes.
Preventing and Managing Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar, is another common issue for individuals with diabetes. It can result from overeating, stress, illness, or insufficient medication. Symptoms include frequent urination, increased thirst, and fatigue.
Regular sugar testing allows you to identify high blood sugar levels and take corrective actions, such as adjusting your diet, increasing physical activity, or modifying your medication. Consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice on managing hyperglycemia.
Mental Health and Diabetes Management
Managing diabetes can be stressful and emotionally taxing. Regular sugar testing, while crucial, can sometimes feel overwhelming. It's essential to prioritize your mental health and seek support when needed.
Join support groups, talk to a mental health professional, or engage in activities that help reduce stress. Remember, managing diabetes is a marathon, not a sprint. Taking care of your mental well-being is just as important as monitoring your blood sugar levels.
Conclusion
Regular sugar testing is a cornerstone of effective diabetes management. It provides valuable insights into how your lifestyle choices, medications, and activities impact your blood sugar levels. By monitoring consistently and making informed decisions, you can lead a healthier, more balanced life.
Take the first step towards better diabetes management today. Prioritize regular sugar testing, follow a balanced diet, stay active, and seek support when needed. Together, these strategies will empower you to take control of your health and thrive despite diabetes.
WANT TO BOOK HEALTH CHECKUP ?
Categories
Top tests
114
Lifestyle Packages
47
Diabetes
58
Preventive Health Checkup
60
Infectious
1
Heart Disease & Hypertension
38
Genomics
1
Others
81
Pulmonary / Infectious
1
Genetics
1
Gastrointestinal / Skeletomuscular
2
Blood Banking & Transfusion
16
Vitamin Deficiency
12
Allergy
9
Blood Disorders
3
Fever
4
Profile
1
Kidney Disease
8
Thyroid Disorder
5
Liver Disease
6
Anemia
5
Arthritis
4
Infertility
6
PCOD
3
Bone Health
1
Cancer
1
Fatty Liver
1