Condition
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Infectious
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Genomics
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Pulmonary / Infectious
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Others
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Others
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Others
- Genetics
- Others
- Gastrointestinal / Skeletomuscular
- Gastrointestinal / Skeletomuscular
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Lifestyle Packages
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Blood Banking & Transfusion
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Allergy
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Others
- Blood Disorders
- Top tests
- Others
- Others
- Others
- Fever
- Fever
- Blood Disorders
- Blood Disorders
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Profile
- Kidney Disease
- Kidney Disease
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Thyroid Disorder
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Allergy
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Liver Disease
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Liver Disease
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Anemia
- Anemia
- Anemia
- Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Anemia
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Thyroid Disorder
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Fever
- Allergy
- Liver Disease
- Lifestyle Packages
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Arthritis
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Kidney Disease
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Allergy
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Kidney Disease
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Allergy
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Allergy
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Infertility
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Allergy
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Top tests
- Infertility
- Top tests
- Thyroid Disorder
- Top tests
- Allergy
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Infertility
- Lifestyle Packages
- Diabetes
- Liver Disease
- Kidney Disease
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Infertility
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Arthritis
- Arthritis
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Vitamin Deficiency
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- Infertility
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- PCOD
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Fever
- PCOD
- Kidney Disease
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Liver Disease
- Thyroid Disorder
- Top tests
- Heart Disease & Hypertension
- PCOD
- Top tests
- Arthritis
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Kidney Disease
- Lifestyle Packages
- Top tests
- Allergy
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Diabetes
- Thyroid Disorder
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Lifestyle Packages
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Top tests
- Kidney Disease
- Liver Disease
- Infertility
- Top tests
- Anemia
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Top tests
- Preventive Health Checkup
- Bone Health
- Cancer
- Fatty Liver

Tests
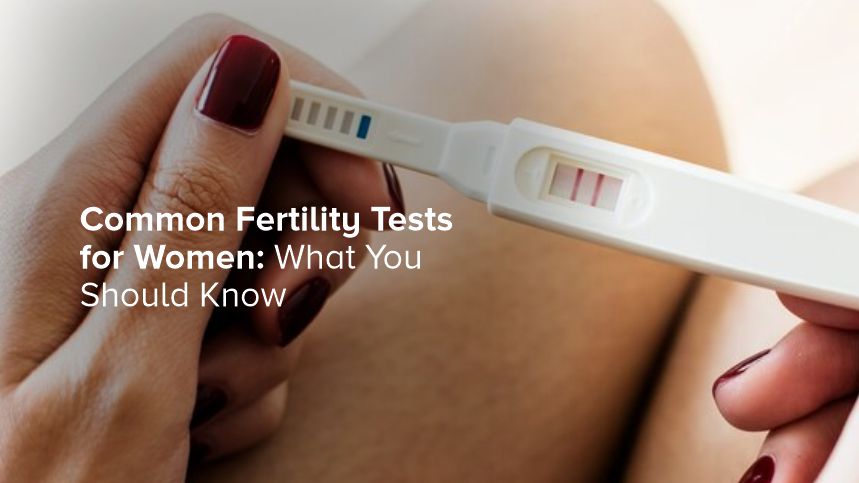
For many women, having children is a deeply personal goal, but the path to parenthood isn’t always straightforward. If you’re facing challenges conceiving or simply want to learn more about your reproductive health, fertility testing can be an insightful starting point. This blog will guide you through the most common fertility tests for women, breaking down why they’re performed, what’s involved, and what the results might mean.
Whether you're just beginning the process or looking for reassurance, understanding these tests can empower you to make informed decisions about your reproductive health.
Why Fertility Testing Matters
Fertility is influenced by a variety of factors, including age, lifestyle, and underlying medical conditions. It’s estimated that about 1 in 8 couples face challenges conceiving—and women often take the initiative to investigate their fertility first. Testing helps not only identify potential issues but also opens the door to tailored treatments that can significantly improve your odds of conception.
If your attempts at conceiving have been unsuccessful for more than 12 months (or 6 months if you're over 35), it may be time to explore fertility testing.
Common Types of Fertility Tests for Women
Below, we explore the most commonly recommended fertility tests, how they work, and what to expect. These tests typically assess hormone levels, egg reserves, and the overall structure of your reproductive organs.
1. Blood Tests for Hormone Levels
Hormonal balance is a critical factor in fertility. Blood tests can detect hormone levels to provide insight into your ovulatory cycle and overall reproductive health.
Key Hormones Tested:
- Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH): High levels of FSH may indicate diminished ovarian reserve, meaning fewer eggs are available for ovulation.
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH): LH plays a significant role in triggering ovulation. Imbalances might signal conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
- Estradiol (E2): This form of estrogen is assessed to evaluate ovarian reserve.
- Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH): AMH levels help estimate ovarian reserve and are considered a reliable marker for understanding how many potential eggs you might still have.
- Thyroid Hormones: Since thyroid function impacts ovulation, abnormal thyroid hormone levels (TSH) can contribute to infertility.
What to Expect:
Blood work is typically drawn on specific days of your menstrual cycle (often between day 2 and day 5). The process involves a quick blood draw and results are usually available within a few days.
2. Pelvic Ultrasound
A pelvic ultrasound provides a visual assessment of your reproductive organs, including the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes.
What It Evaluates:
- Ovarian Health: Physicians can count antral follicles (small "resting" follicles containing eggs) to assess ovarian reserve effectively.
- Uterus: Check for abnormalities like fibroids or polyps that might interfere with implantation or pregnancy.
- Fallopian Tubes: If tube blockage is suspected, a more specific procedure like an HSG (see below) might follow.
What to Expect:
You'll undergo a transvaginal ultrasound, where a small probe is inserted into the vagina for a closer look at your reproductive organs. It’s a painless procedure that typically takes around 20 minutes.
3. Hysterosalpingography (HSG)
An HSG is a specialized X-ray to examine the fallopian tubes and uterine cavity. It checks for blockages or abnormalities that may prevent pregnancy.
Why It’s Performed:
- Fallopian tubes must be open for sperm to reach the egg.
- Uterine abnormalities, such as scarring or deformities, might affect implantation.
What to Expect:
A contrast dye is injected through the cervix, and X-rays are taken to track how the dye moves through the uterus and tubes. While some women may experience mild cramping during the procedure, it’s a quick and straightforward test.
4. Sonohysterography
Also known as saline infusion sonography, this procedure uses saline and ultrasound to get a detailed view of the uterine cavity.
What It Evaluates:
- Uterine abnormalities like polyps, fibroids, or scars (similar to HSG).
- Uterine lining health, which is key to successful implantation.
What to Expect:
Saline is injected into the uterus through a small catheter while the transvaginal ultrasound captures real-time images. The saline helps expand the uterus, allowing doctors to see abnormalities more clearly.
5. Ovulation Testing
Tracking ovulation is crucial when looking at fertility. If you’re not ovulating regularly, conception will be challenging.
Common Tests:
- Basal Body Temperature (BBT): While not a medical test, many women track their BBT at home to detect ovulation patterns.
- Ovulation Predictor Kits (OPKs): These measure LH surges, pinpointing when ovulation is likely.
- Progesterone Blood Test: Done mid-cycle, this test determines if ovulation has occurred.
What to Expect:
BBT and OPKs are at-home options, while the progesterone test involves a quick blood draw ordered by your doctor.
6. Genetic Testing
While not part of routine fertility assessments, genetic testing may be recommended if you’ve faced recurrent pregnancy loss or are considering advanced treatments like IVF.
What It Can Reveal:
- Genetic conditions or mutations that may affect fertility.
- Risk of passing conditions on to offspring.
What to Expect:
This involves a blood or saliva sample, analyzed to identify genetic markers or inherited conditions.
Working With Your Doctor
Fertility testing can feel overwhelming, but your healthcare provider will guide you through the process. Keep a record of your cycle, note any symptoms you’re experiencing, and share these details during your consultation. The more information your doctor has, the more personalized your care plan.
Conclusion
Fertility testing is an essential tool for women trying to conceive or understand their reproductive health. By identifying any potential issues early on, you’re taking proactive steps toward building the future you envision.
If you’re considering fertility testing, speak to your gynecologist or reach out to a fertility specialist. They’ll help prioritize the right tests for your unique situation, ensuring the most effective route to parenthood.
The path to parenthood may not always be easy, but knowledge is power—and fertility testing can provide the clarity you need to move forward with confidence.
WANT TO BOOK HEALTH CHECKUP ?
Categories
Top tests
114
Lifestyle Packages
47
Diabetes
58
Preventive Health Checkup
60
Infectious
1
Heart Disease & Hypertension
38
Genomics
1
Others
81
Pulmonary / Infectious
1
Genetics
1
Gastrointestinal / Skeletomuscular
2
Blood Banking & Transfusion
16
Vitamin Deficiency
12
Allergy
9
Blood Disorders
3
Fever
4
Profile
1
Kidney Disease
8
Thyroid Disorder
5
Liver Disease
6
Anemia
5
Arthritis
4
Infertility
6
PCOD
3
Bone Health
1
Cancer
1
Fatty Liver
1